Decentralized Sparse Gaussian Process Regression
Summary
This paper presents a decentralized sparse Gaussian process regression (SGPR) framework designed for real-time, multi-agent environments. It introduces a novel radial clustering algorithm that enables SGPR models to adapt the number and location of inducing points based on data distribution. This improves estimation accuracy in dynamic settings and allows the model to operate efficiently under strict onboard hardware and communication constraints.
Key contributions include:
- A clustering algorithm that adaptively selects inducing point locations.
- A provable upper bound on the number of inducing points.
- An event-triggered mechanism for updating inducing points in response to new data.
- A message-passing strategy that supports low-bandwidth, multi-agent coordination.
Figure
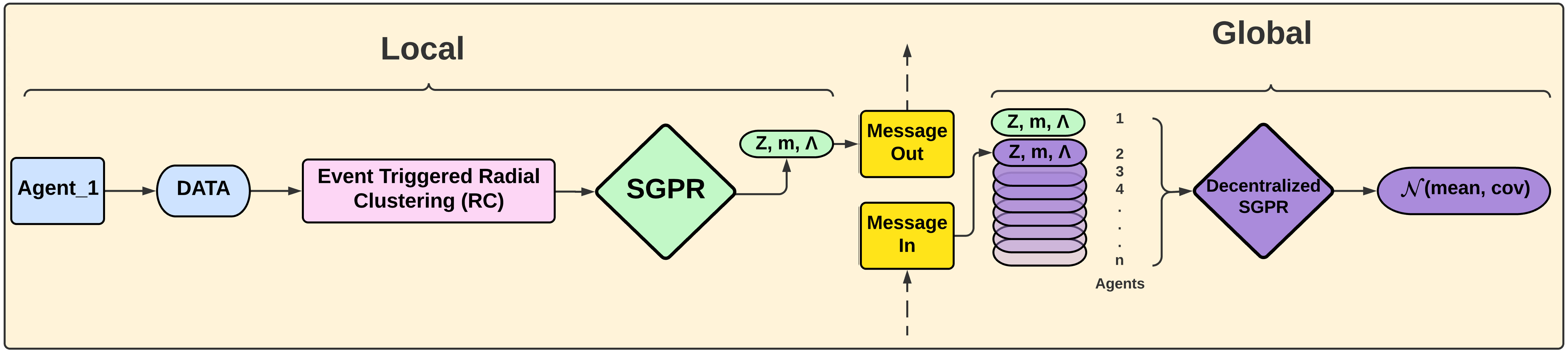
Figure: Adaptive inducing point generation and decentralized estimation architecture.
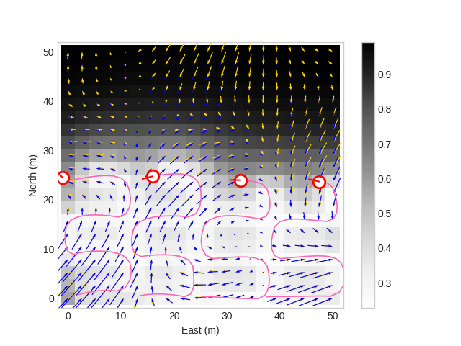
Figure: Four agents fuse measurements using DSGPR to estimate wind field.
Abstract
In this paper, we present a decentralized sparse Gaussian process regression (DSGPR) model with event-triggered, adaptive inducing points. We address common issues inherent in decentralized frameworks such as high computation costs, inter-agent message bandwidth restrictions, and data fusion integrity. We also improve real-time sparse Gaussian process regression models by introducing an adaptation of the mean shift and fixed-width clustering algorithms called radial clustering. Radial clustering enables real-time SGPR models to have an adaptive number of inducing points through an efficient inducing point selection process. The entire DSGPR framework is evaluated on multiple simulated random vector fields. The results show that this framework effectively estimates vector fields using multiple autonomous agents. We also show the practical use of these algorithms by testing them on hardware typical for small autonomous vehicles.
Citation
Norton, Tanner, et al.
“Decentralized Sparse Gaussian Process Regression with Event-Triggered Adaptive Inducing Points.”
Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, vol. 108, no. 4, 2023, article 72.
Link to Article
